Ep1: 'Goal to $15000' - Path to Developed Nation
A series explaining how India is progressing towards the target of achieving Developed nation goal by 2047
Welcome to Ep1 of Path to Developed Nation - The Goal to reach the per-capita of developed nation by 2047.
PM Modi announces vision to turn India into a developed nation over the next 25 years
But is it that easy? are we in the right track to achieve it ?
Where are we placed currently ? and how we can reach to a developed nation status.
And today, we tell you all about India’s ambitions and the hurdles in its path to achieve this target.
But First… Why Per capita is a important metric?
A developed economy is typically characteristic of a developed country with a relatively high level of economic growth and security.
Standard criteria for evaluating a country's level of development are income per capita or per capita gross domestic product, the level of industrialization, the general standard of living, and the amount of technological infrastructure.
✔ Countries with relatively high levels of economic growth and security are considered to have developed economies.
✔Common criteria for evaluation include income per capita or per capita gross domestic product.
✔If per capita gross domestic product is high but a country has poor infrastructure and income inequality, it would not be considered a developed economy.
But hang on a minute… 15000($) (PPP) ?
Yes, Some economists consider $12,000 to $15,000 per capita GDP to be sufficient for developed status while others do not consider a country developed unless its per capita GDP is above $25,000 or $30,000.
The U.S. per capita GDP in 2019 was $65,111 and we are at $2,850
In 2022, India's per capita income (nominal) was $2,850. This means that India would need to more than quadruple its per capita income in order to reach developed-nation status.
In 1991, India stood on the precipice of economic stagnation.
Its per capita income was a mere $490 (nominal), ranking it among the poorest countries in the world. The economy was heavily regulated, stifling innovation and hindering growth.
However, a turning point arrived with the adoption of economic liberalization policies, ushering in a new era of openness and opportunity.
The liberalization of India's economy in 1991 marked the beginning of a transformative journey. Several factors coalesced to drive India's economic surge and fuel its ascent to a middle-income status.
Economic Liberalization: The dismantling of protectionist barriers and the embrace of foreign investment and trade opened up new avenues for growth and investment. This shift unleashed India's untapped potential and set the stage for rapid economic expansion.
Infrastructure Development: India embarked on a massive infrastructure building spree, investing heavily in roads, railways, ports, and power generation. This infrastructure overhaul improved connectivity, reduced transportation costs, and facilitated the movement of goods and people, boosting productivity and economic activity.
Demographics Advantage: India's demographic profile, characterized by a young and growing population, presented a unique opportunity. This demographic dividend provided a large pool of potential workers, fueling labor-intensive industries and contributing significantly to economic growth.
Education and Skill Development: India recognized the importance of human capital and made significant investments in education and skill development. This focused effort enhanced the productivity of the workforce, making India more attractive to businesses seeking skilled labor.
And after 24 Year the journey has been remarkable, transforming the country from a nation struggling with poverty to a rising economic powerhouse and to point it out.
India's per capita income has increased by over 20x since the early 1990s, when it stood at just $490 (nominal). This remarkable growth is testament to the country's economic reforms and its entrepreneurial spirit.
and what’s more even interesting is Between 2010 and 2022, India's per capita income grew by an average of 6.7% per year, compared to 2.1% for the US.
We can easily see that India’s GDP per capita is growing steadily y-o-y but there were time when it went towards the negative side as well (covid for example in 2020).
In short the path is not a straight line, so its going to be a testament of how India will overcome all those upcoming challenges.
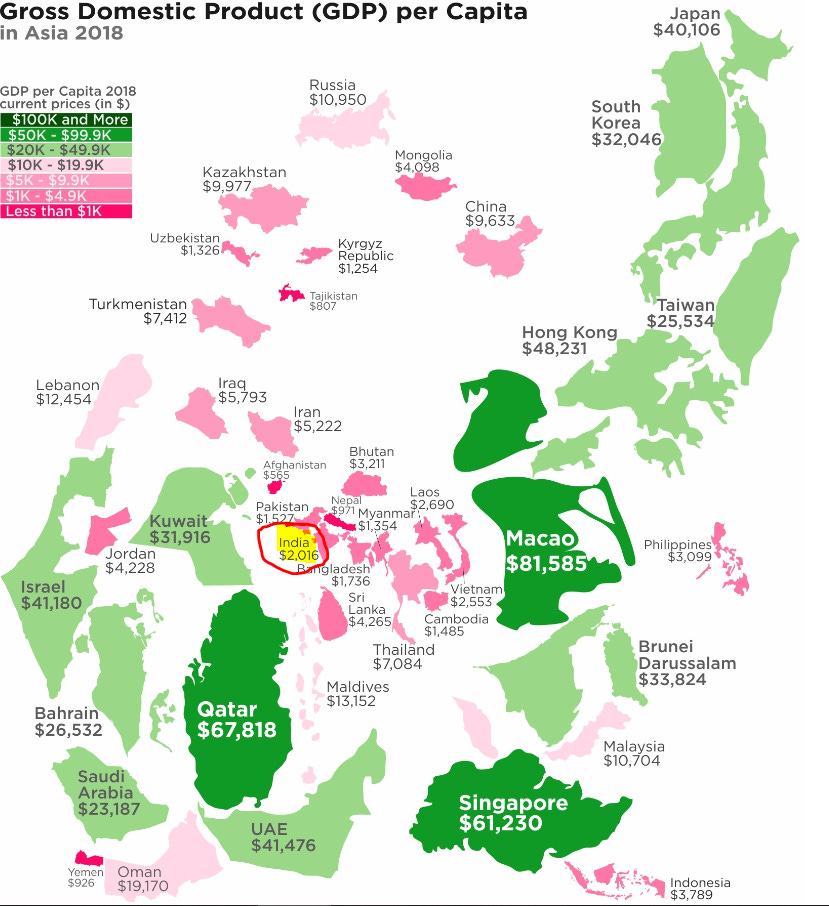
In a overall Asia perspective,
China has also experienced rapid economic growth and a significant increase in per capita income.
However, India's growth rate has been faster than China's in recent years.
India is catching up quickly. India's per capita income has been growing at an average rate of 6.7% per year since 2010, while China's per capita income growth has slowed to 4.4% per year. If India can continue to grow at its current pace, it is expected to surpass China's per capita income in the next few decades.
but how did china improve so quickly?
… and what can we learn good parts as well from their mistakes.
China has achieved remarkable economic growth over the past few decades, lifting hundreds of millions of people out of poverty. There are many lessons that other countries can learn from China's experience, both in terms of successes and mistakes.
Key Lessons from China's Successes:
Economic Reforms: China's economic reforms, which began in the late 1970s, were essential for its economic growth. These reforms included opening up the economy to foreign investment, privatizing state-owned enterprises, and liberalizing trade.
Focus on Infrastructure: China has invested heavily in infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and power generation. This has improved connectivity and reduced transportation costs, which has boosted productivity.
Massive Education Campaign: China has made a massive investment in education, which has helped to improve the skills of the workforce. This has made China more attractive to businesses and helped to boost productivity.
Embrace of Technology: China has embraced technology and has become a major player in the global technology sector. This has helped to drive economic growth and create new jobs.
Key Lessons from China's Mistakes:
Environmental Impact: China's rapid economic growth has come at a significant environmental cost. The country is now the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases.
Income Inequality: China's economic growth has not been evenly distributed. The gap between the rich and the poor has widened, leading to social unrest and instability.
Human Rights Abuses: China has been accused of human rights abuses, including forced labor, mass surveillance, and crackdowns on dissent.
Political Repression: China has a one-party communist government that tightly controls all aspects of society. This has led to concerns about the lack of democracy and freedom in the country.
Overall, China's experience provides both positive and negative lessons for other countries. Countries can learn from China's successes in terms of economic reforms, infrastructure investment, education, and technology adoption. However, they should also be aware of the potential environmental, social, and political costs of rapid economic growth.
Here are some specific examples of how India can learn from China's successes and mistakes:
Economic Reforms: India can further liberalize its economy and open it up to foreign investment. It can also privatize some state-owned enterprises and reduce the role of government in the economy.
Infrastructure Investment: India can invest more heavily in infrastructure, particularly in rural areas. This will improve connectivity and reduce transportation costs, which will boost productivity and economic growth.
Education: India can invest more in education, particularly in vocational training. This will improve the skills of the workforce and make India more attractive to businesses. Semiconductor manufacturing / Solar panels / EV are some of the emerging industries which India could tap on.
Technology Adoption: India can encourage the adoption of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and robotics. This will help to drive economic growth and create new jobs.
Environmental Protection: India can adopt more stringent environmental regulations and invest in renewable energy sources. This will help to mitigate the environmental impact of economic growth.
Social Justice: India can address the issue of income inequality by investing in social programs and providing more opportunities for the poor.
Political Reform: India can gradually introduce political reforms to increase transparency, accountability, and public participation. This will help to create a more democratic and just society.
How the road looks ahead for India and what are the challenge that it needs to overcome to keep growing.
Despite its remarkable achievements, India faces several challenges as it strives to achieve its full economic potential.
Addressing Infrastructure Bottlenecks: India still grapples with infrastructure bottlenecks, particularly in urban areas. These bottlenecks hinder economic growth, limit access to essential services, and pose challenges for businesses and individuals alike.
Wars and Bilateral ties : Growing concerns within Asia (china border issues, Maldives recent ties, Pakistan (militants/Terrorist issues) and War across globe will have an impact on India’s growth story.
Creating Employment Opportunities: India's growing population and expanding workforce demand a robust job creation engine. To achieve sustainable growth, India must continue to diversify its economy beyond its traditional sectors and promote innovation to create new employment opportunities.
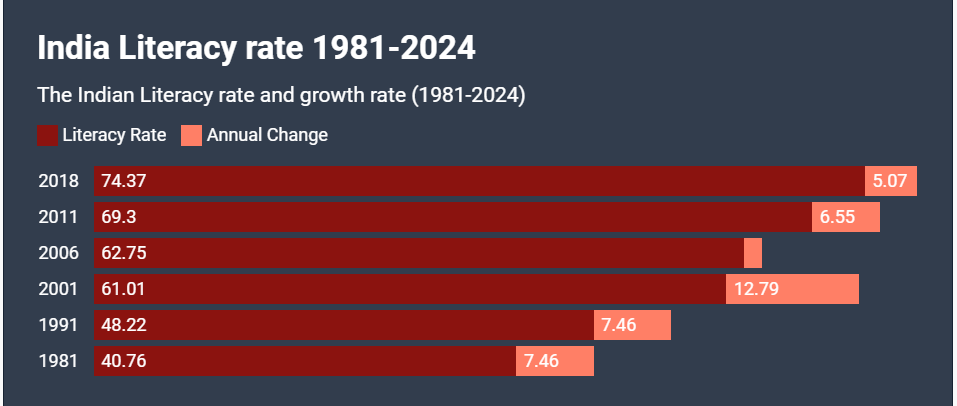
Skill Development + Literacy in the 21st Century:
To remain competitive in the global economy, India must invest in the continuous education and skill development of its workforce. Improve the literacy rate by improving the quality of educations.This will equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary to thrive in the evolving demands of the 21st-century economy.
Read more on India Skill Report 2023
Bridging Inequality Gaps: India's economic growth has not been evenly distributed, leading to a widening gap between the rich and the poor. Addressing inequality is crucial for achieving sustainable and equitable economic growth.
More than 40% of the wealth created in the country from 2012 to 2021 had gone to just 1% of the population while only 3% had trickled down to the bottom 50%
India's per capita income journey has been remarkable, transforming the country from a nation struggling with poverty to a rising economic powerhouse.
While challenges remain, India is well-positioned for continued growth in the coming years.
By addressing infrastructure bottlenecks, creating employment opportunities, investing in skill development, and bridging inequality gaps, India can continue its ascent to becoming a developed nation. The future of India's per capita income is bright, with the potential to reach new heights and bring prosperity to its citizens.
As per PWC report💹💹💹
Twenty-five years from now, India could exceed a per capita income of USD 26,000 – almost 13 times the current level – by unlocking some key areas that demand both investments and policy interventions.
This is it !